Services
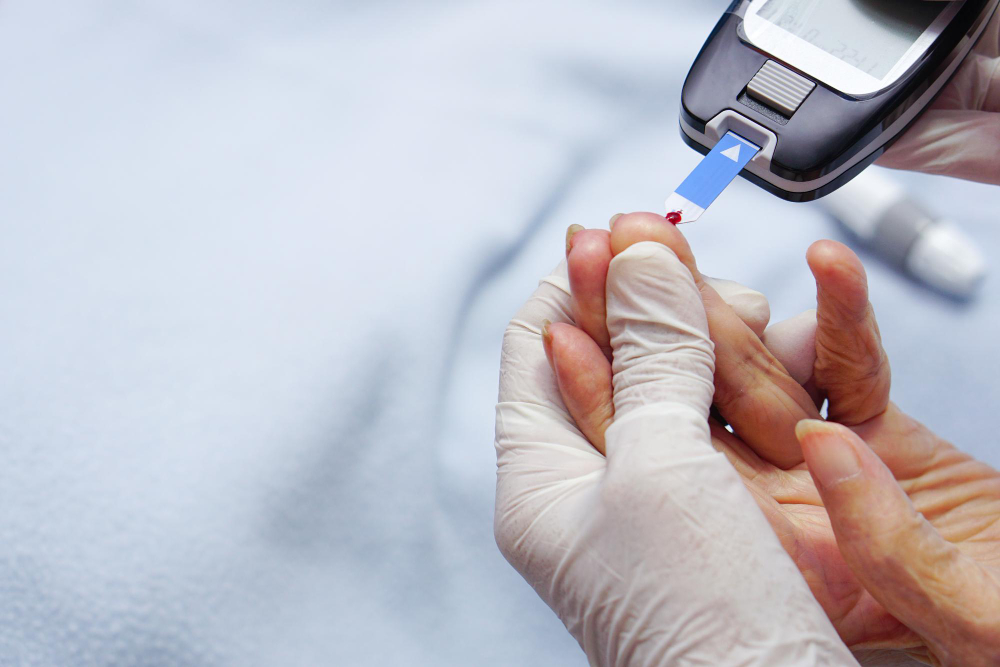
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin use. It can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Managing diabetes requires lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
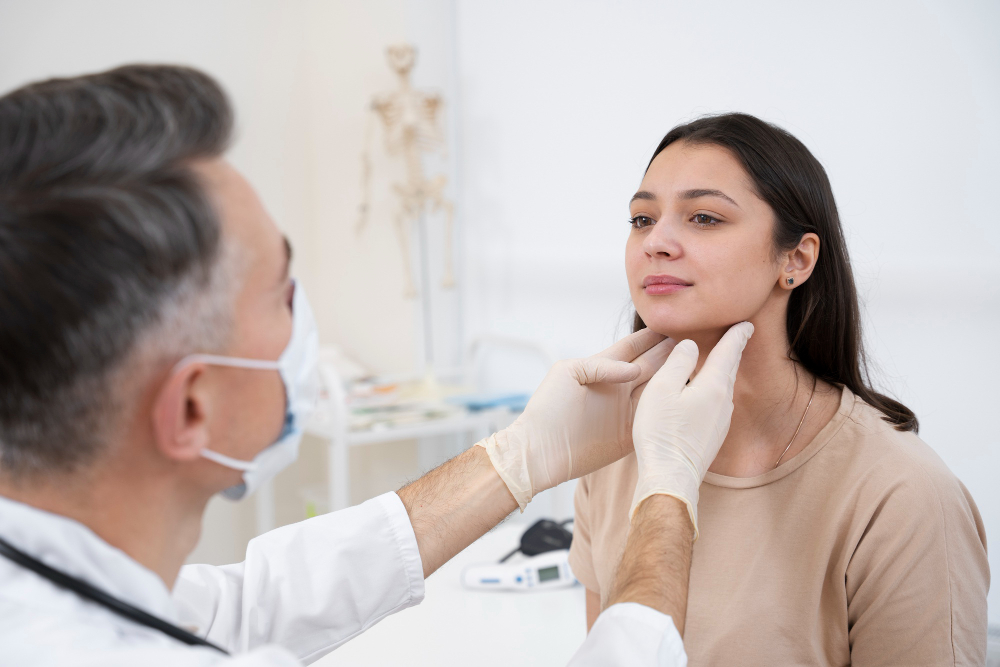
Thyroid
Thyroid disorders involve dysfunction of the thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism through hormone production. Conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, and mood fluctuations. Proper diagnosis and treatment, including medication or lifestyle adjustments, are crucial for maintaining hormonal balance.
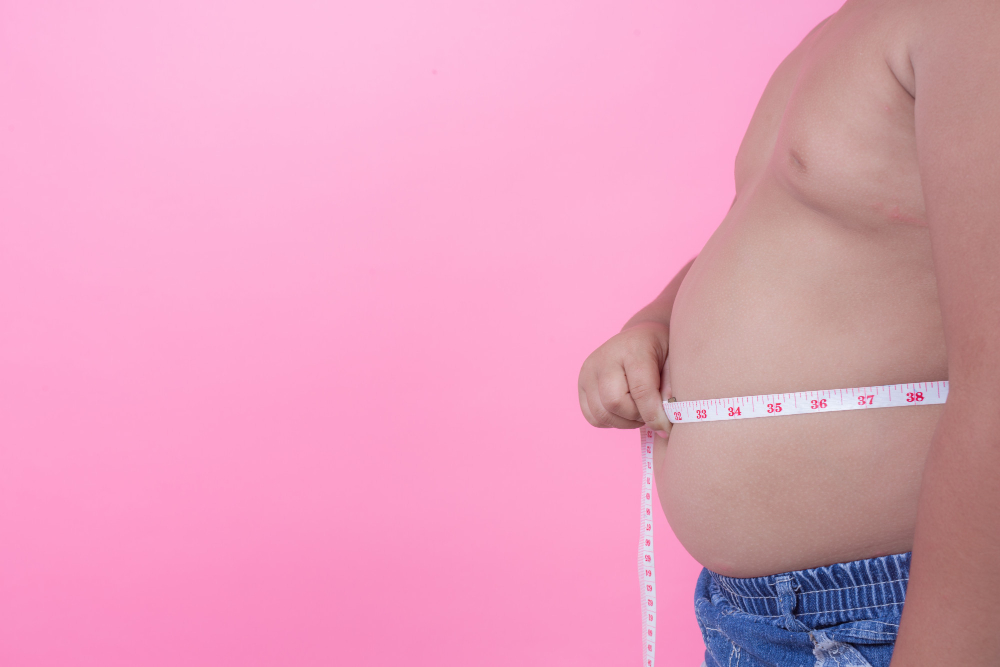

Obesity
Obesity is defined as having an excessive amount of body fat, often measured by body mass index (BMI). It increases the risk of developing chronic conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. A comprehensive approach to treatment includes lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and physical activity to promote weight loss.

Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. It includes high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Early detection and lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and dietary changes, are essential for managing this syndrome.

Pubertal disorders
Pubertal disorders affect the timing and progression of puberty, resulting in conditions like precocious puberty or delayed onset. These disorders can impact physical growth, sexual development, and emotional health in adolescents. Diagnosis often involves hormone assessments and may require treatment to regulate development and support overall well-being.

Metabolic bone disease
Metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and osteomalacia, result from imbalances in bone remodeling, leading to weakened bones and increased fracture risk. Contributing factors may include hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and lack of physical activity. Treatment typically involves lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medications to strengthen bone health.

Child growth-related problems
Child growth-related problems encompass various issues that can hinder a child's physical development, such as growth hormone deficiencies or nutritional deficiencies. Early identification and intervention are crucial for addressing these issues. Treatment may include hormone therapy, nutritional support, and regular monitoring to ensure children reach their optimal growth potential.

Hypertension in Young Adults
Hypertension in young adults is increasingly common and can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Factors such as obesity, stress, and sedentary lifestyles contribute to elevated blood pressure. Lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and medication, may be necessary to manage and reduce long-term health risks associated with hypertension.

Dyslipidemia / Hypercholesterolemia
Dyslipidemia, characterized by abnormal lipid levels, includes high cholesterol and triglycerides. This condition increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Contributing factors include poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, such as a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, alongside medications to manage cholesterol levels effectively.

Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk. It often occurs silently, with no symptoms until a fracture occurs. Risk factors include aging, hormonal changes, and inadequate calcium or vitamin D intake. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, medications, and supplements to strengthen bone health.
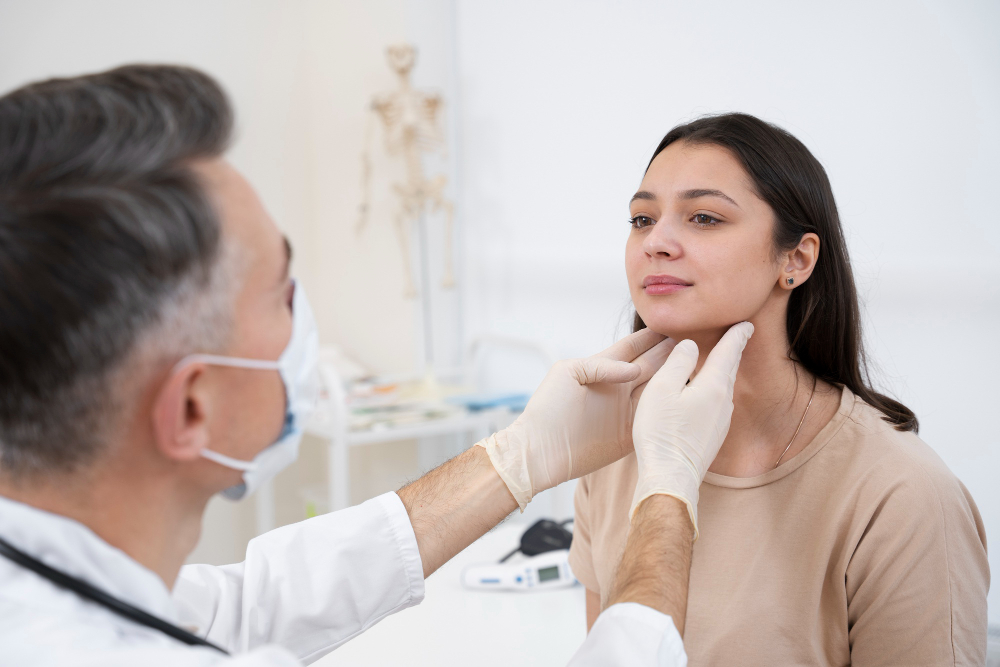
parathyroid disorders
Parathyroid disorders, including hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism, affect calcium regulation in the body. Symptoms may include bone pain, fatigue, and muscle weakness. Diagnosis often involves blood tests to measure calcium and parathyroid hormone levels. Treatment may require medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, depending on the disorder's severity and underlying causes.
Pituitary-adrenal
Pituitary-adrenal disorders involve dysregulation of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands, impacting hormone production. Conditions such as Cushing's syndrome or Addison's disease can lead to significant health issues. Diagnosis includes hormone level assessments and imaging studies. Treatment typically involves medication or surgery to restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms.
All hormonal problems and endocrine malignancies
Hormonal problems and endocrine malignancies encompass a range of conditions affecting hormone-producing glands, including thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary disorders. Symptoms vary widely and may include weight changes, fatigue, and mood disturbances. Comprehensive evaluation and treatment are essential, often involving hormone replacement therapy, medication, or surgical intervention for malignancies.

Sexual dysfunction in men
Sexual dysfunction in men refers to difficulties related to sexual performance, including erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, or low libido. Various factors contribute, including psychological, hormonal, or vascular issues. Effective treatment options range from counseling and lifestyle changes to medication and therapy, addressing both physical and emotional aspects of sexual health.

Hormonal aspects of unwanted hair growth in women
Unwanted hair growth in women, often related to hormonal imbalances like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or adrenal disorders, can cause distress. Diagnosis involves evaluating hormone levels and underlying conditions. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, hormonal therapies, and cosmetic interventions to manage hair growth and enhance overall well-being.
Irregular menses (PCOS) and Male infertility
Irregular menses, commonly associated with PCOS, can lead to fertility challenges in women. In men, infertility may stem from hormonal imbalances or other underlying conditions. Diagnosis involves comprehensive evaluations, including hormone testing and imaging. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, medication, and assisted reproductive technologies to support family planning.
